Mastering Remote IoT: A Comprehensive Guide To Effortless Device Management
In today's hyper-connected world, the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to revolutionize how we interact with technology. The ability to remotely access and manage IoT devices has become a necessity for both individuals and businesses alike. Remote IoT solutions provide an unparalleled level of convenience, allowing users to connect and control their devices from virtually anywhere. This guide will delve into the intricacies of using remote IoT systems effectively, particularly focusing on navigating the challenges of accessing IoT devices behind a router without requiring a MAC address. As we explore the nuances of remote IoT, we will also examine its broader implications on society and the technology industry.
Before we dive into the technical aspects, it is essential to understand what remote IoT entails. At its core, remote IoT refers to the ability to access and control IoT devices over the internet from a remote location. While this concept may seem straightforward, several obstacles can arise when attempting to establish such connections. One of the most common hurdles is accessing IoT devices behind a router without an external IP address. This challenge becomes even more pronounced when MAC address filtering is enabled on the router, adding an additional layer of complexity. Fortunately, there are proven methods to overcome these obstacles, ensuring seamless connectivity while maintaining robust security measures.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Name | Connor Calderwood |
| Date of Publication | April 25, 2025 |
| Profession | Technology Consultant |
| Area of Expertise | IoT Solutions and Remote Connectivity |
| Notable Achievements | Published several research papers on IoT security and connectivity |
| Reference Website | https://www.remoteiotguide.com |
One of the simplest ways to bypass MAC address restrictions is to disable MAC address filtering entirely. While this may seem counterintuitive from a security perspective, it can be a viable solution when coupled with other safeguards. To disable MAC address filtering, users must first log in to their router's admin interface using the default gateway IP address, typically 192.168.1.1. Once inside, navigate to the security settings section and locate the MAC address filtering option. By disabling this feature, users can eliminate one of the primary barriers to accessing IoT devices remotely. However, it is crucial to implement alternative security measures, such as encryption and strong password protocols, to ensure the network remains secure.
- Jelly Rolls Arrests The Untold Story What You Didnt Know
- Iowa Court Forms Legal Resources Your Guide To Free Access
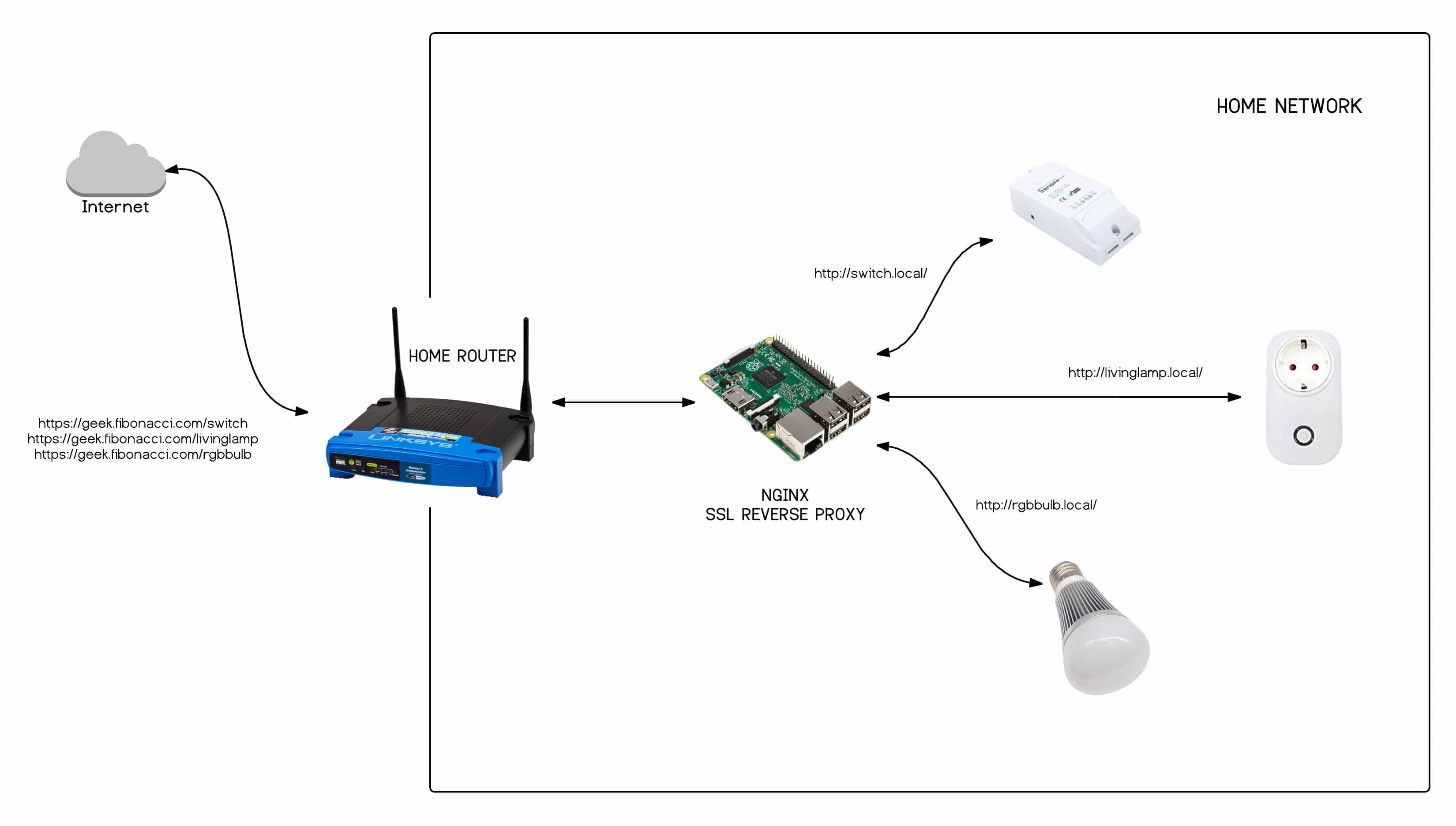
Another effective method for accessing IoT devices behind a router involves configuring port forwarding. This process involves mapping specific ports on the router to the private IP addresses assigned to individual IoT devices. For example, if a user wishes to remotely access a Raspberry Pi, they can forward TCP port 22 (the default SSH port) to the device's private IP address. By doing so, users can establish secure SSH connections to their devices without requiring an external IP address or MAC filtering. Additionally, leveraging cloud platforms like AWS IoT Core or Microsoft Azure IoT Hub can further enhance the manageability and scalability of remote IoT systems.
The demand for remote IoT solutions has surged in recent years, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing prevalence of smart devices. From smart thermostats and security cameras to industrial sensors and medical devices, the applications of IoT are virtually limitless. However, this rapid growth has also raised concerns about data privacy and security. High-profile incidents involving hacked IoT devices have underscored the importance of implementing robust security measures when designing remote IoT systems. Industry leaders, including Elon Musk and Tim Cook, have publicly emphasized the need for greater transparency and accountability in IoT security practices.
For those seeking to access IoT devices remotely without relying on Windows or incurring additional costs, there are several free and open-source tools available. One such tool is Pinggy, which enables remote SSH access to devices like Raspberry Pi without requiring port forwarding. By utilizing cloud-based infrastructure, Pinggy eliminates the need for complex router configurations while maintaining a high level of security. Furthermore, the platform offers a user-friendly interface, making it accessible to individuals with varying levels of technical expertise.
- Gypsy Rose Blanchard From Prison To Freedom What You Need To Know
- Flix Stadium 10 Showtimes Tickets More Lancaster Ny
When considering the broader implications of remote IoT, it is important to recognize its potential impact on society. The ability to remotely manage IoT devices has the power to transform industries ranging from healthcare to agriculture. For instance, remote IoT systems can enable doctors to monitor patients' vital signs in real-time, improving diagnostic accuracy and reducing hospital readmissions. Similarly, farmers can leverage IoT sensors to optimize irrigation systems, conserving water and increasing crop yields. However, these advancements must be balanced with ethical considerations, ensuring that the benefits of remote IoT are equitably distributed across society.
In addition to its practical applications, remote IoT has also sparked a wave of innovation within the technology sector. Startups and established companies alike are investing heavily in IoT research and development, driving the creation of cutting-edge solutions. One notable example is the emergence of edge computing, which allows data processing to occur closer to the source, reducing latency and improving performance. This shift has significant implications for remote IoT, as it enables more efficient and reliable device management. Industry leaders such as Amazon, Google, and Microsoft are at the forefront of this movement, collaborating with academic institutions and government agencies to advance the field.
As the adoption of IoT devices continues to grow, so too does the importance of addressing associated challenges. One of the most pressing issues is the potential for cyberattacks targeting vulnerable IoT systems. To mitigate this risk, organizations must prioritize security from the outset, incorporating best practices such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular firmware updates. Furthermore, fostering collaboration between stakeholders, including manufacturers, regulators, and end-users, is essential to creating a safer and more resilient IoT ecosystem.
Returning to the technical aspects of remote IoT, it is worth noting that not all challenges can be resolved through router configurations or cloud platforms. In some cases, users may need to explore alternative solutions, such as using a virtual private network (VPN) or deploying a dedicated IoT gateway. These approaches offer enhanced security and flexibility, albeit at the cost of increased complexity. For those willing to invest the time and effort, the rewards can be significant, enabling seamless connectivity and streamlined device management.
In conclusion, mastering remote IoT requires a combination of technical expertise, strategic planning, and a commitment to security. By understanding the underlying principles of IoT networks and implementing proven solutions, users can overcome the challenges associated with accessing devices behind a router. As the technology continues to evolve, the opportunities for innovation and growth are boundless. However, it is imperative that we approach this evolution with caution, ensuring that the benefits of remote IoT are realized responsibly and equitably. For further insights into this fascinating field, readers are encouraged to explore authoritative resources such as the IEEE or the IoT Security Foundation.
- Great Falls Mt Garage Moving Sales Find Deals More
- Dantehall Remembering The Gospel Singer Latest News Updates
How To Use Remote IoT Behind Router Mac Without A Comprehensive Guide
How To Use Remote IoT Behind Router MAC Free A Comprehensive Guide
How To Use Remote IoT Behind Router MAC Free A Comprehensive Guide